How Can We Help?
Content metadataContent metadata
Any content submitted into Pure has an editor window with a range of menu points. This section describes the menu points for the Research Output editor window:
EDIT |
|---|
Metadata
Mandatory fields are marked with a red asterisk (*) .These fields must be filled before the content can be saved.
| Metadata section | Description | Scenarios | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Publication category* | Categorize content according to intended target audience. Indicate if peer reviewed or not. | This is configurable by Administrators of Pure, so options may differ per content type. | |||||||||
| Contributors and affiliations* | Add internal/external contributors and affiliations, and author collaborations. |
When adding content produced prior to current affiliation.
|
|||||||||
| Publication Managed by* | This organization unit will handle the approval or validation of the content using a Workflow. | Added automatically for Personal users, based on the current affiliation. | |||||||||
| Journal / Publisher* | Relation to journal or publisher who has published the content. |
Optionally, Sherpa RoMEO colors can be highlighted upon selection. This will indicate publishing policies of journal or publisher, which is needed when uploading electronic version. See below. Note, Sherpa RoMEO colors need to be enabled by Administrators of Pure. Note: The Sherpa RoMEO colors have now been deprecated as Sherpa Romeo have updated their Open Access policy recommendations for journals. To check and review a journal's policies, please go to the Sherpa Romeo website and search using this journal's ISSN(s). |
|||||||||
| Electronic version upload | Upload or link to the actual full text of the article, or to related files. |
|
|||||||||
|
Full text accessible openly via Portal / Web service / Backend, or via external site (e.g. via DOI)
|
||||||||||
| Keywords | Used to categorize the content by either structured and/or free text keywords. | The actual keywords to select from can be configured by Administrators of Pure. | |||||||||
| Notes, Bibliographical note | For information not fitting into existing fields. | ||||||||||
| Relations | Other content from Pure that can be related to submissions. | Can be useful to relate e.g. a Part I and II of articles. | |||||||||
| Visibility | Can be set to Public, Campus, Backend or Confidential |
There might be 'sensitive' data that the institution might want to limit access to. Also, this might be affected by institutional policies. |
|||||||||
| External publication IDs | Identifier from the content import source so that the content can be traced back. | For example Scopus ID, Pubmed ID, Web of Science ID. |
Metrics
Metrics can include
- citations from Scopus, SciVal or Web of Science
- journal-specific metrics such as Impact factor or CiteScore.
In the example below citation data is from Scopus and metrics on the related journal are Scopus metrics of CiteScore, SJR, SNIP.
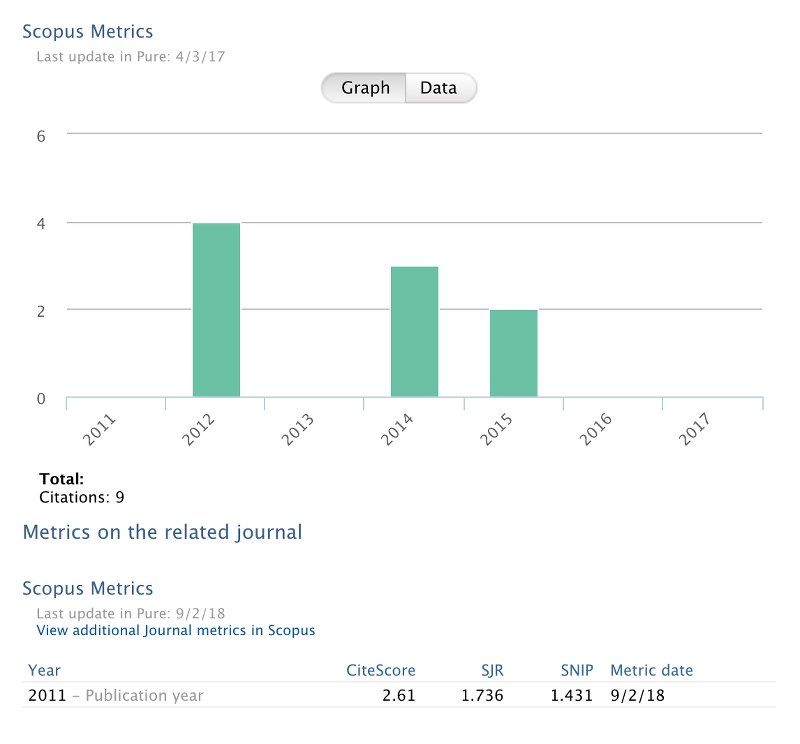
The actual metrics shown depend on institutional selection.
OVERVIEW |
|---|
Relations
This section provides details of how a given piece of content relates to other content.
Fingerprints
|
See Fingerprinting - Core Principles Fingerprinting for detailed information about fingerprinting and fingerprints. |
Optional. May not be present in your current Pure.
This section provides an overview of aggregated fingerprints for this research output. More information on Fingerprints can be found here: Elsevier Fingerprint Engine.
Display
Shows the metadata in selected formats. The detailed format is set as default, but other formats are available (APA, Harvard, Vancouver etc.)
System info-tab is used to show Pure system data, as date and creator of the content, related IDs etc. It also contains Mods.
HISTORY AND COMMENTS |
|---|
History and comments
Comments
Can be used to inform related co-authors, editors or administrators of the content using the 'Write a comment about the content'. From here, recipients can be selected.
History
Is a log of changes/actions applied to the content.
Additional editor window features
Workflow
Workflow is used to determine who has the current responsibility of finalizing the content in each step. Finalizing can mean different things depending on the workflow step and/or local strategies.
This section is written from the perspective of a Personal User. For a Personal User, finalizing usually means adding as much relevant metadata as possible before handing the submission over for quality assurance.
Personal Users can use two workflow steps:
| Workflow Step | What it means | Additional notes |
|---|---|---|
| Entry in progress | When a piece of content has been created it will be continuously editable in this step. This means that it can be saved, modified, saved, modified etc. until no more details can be added to the metadata. |
All "Entries in Progress" are displayed as tasks in the Personal tasks area. All content created by Personal users will remain an "Entry in Progress" until a Pure Administrator or Editor validate the content and data quality. |
| For validation* | Once no more metadata can be added, the content can be saved in this state. This will then hand over the responsibility of validating* the content (finalizing data quality assurance) to the Editors of research output. | By default, once validated* the content becomes non-editable by the Personal User. |
*This is true in the 3-step workflow. If 4 steps are used, this step is called 'For approval', and Editors need to Approve the content.
Change template
When a publication has been imported from an external source and is incorrectly mapped to the desired publication type, the Personal User can change the template to an appropriate one. The already completed metadata fields are transferred to the corresponding ones in the new type. However, some fields may not be mapped. For example, when changing from something published in a journal to something NOT published in a journal. In this case, the Journal information is not transferred but the information is still preserved for future reference in the History and comments section.
Disclaim
If a Personal User has been incorrectly associated with a research output, they cannot remove their association on their own. They can use the "Disclaim" button to flag the wrong association. Designated users will then be prompted to make appropriate corrections.
Published at December 15, 2023
